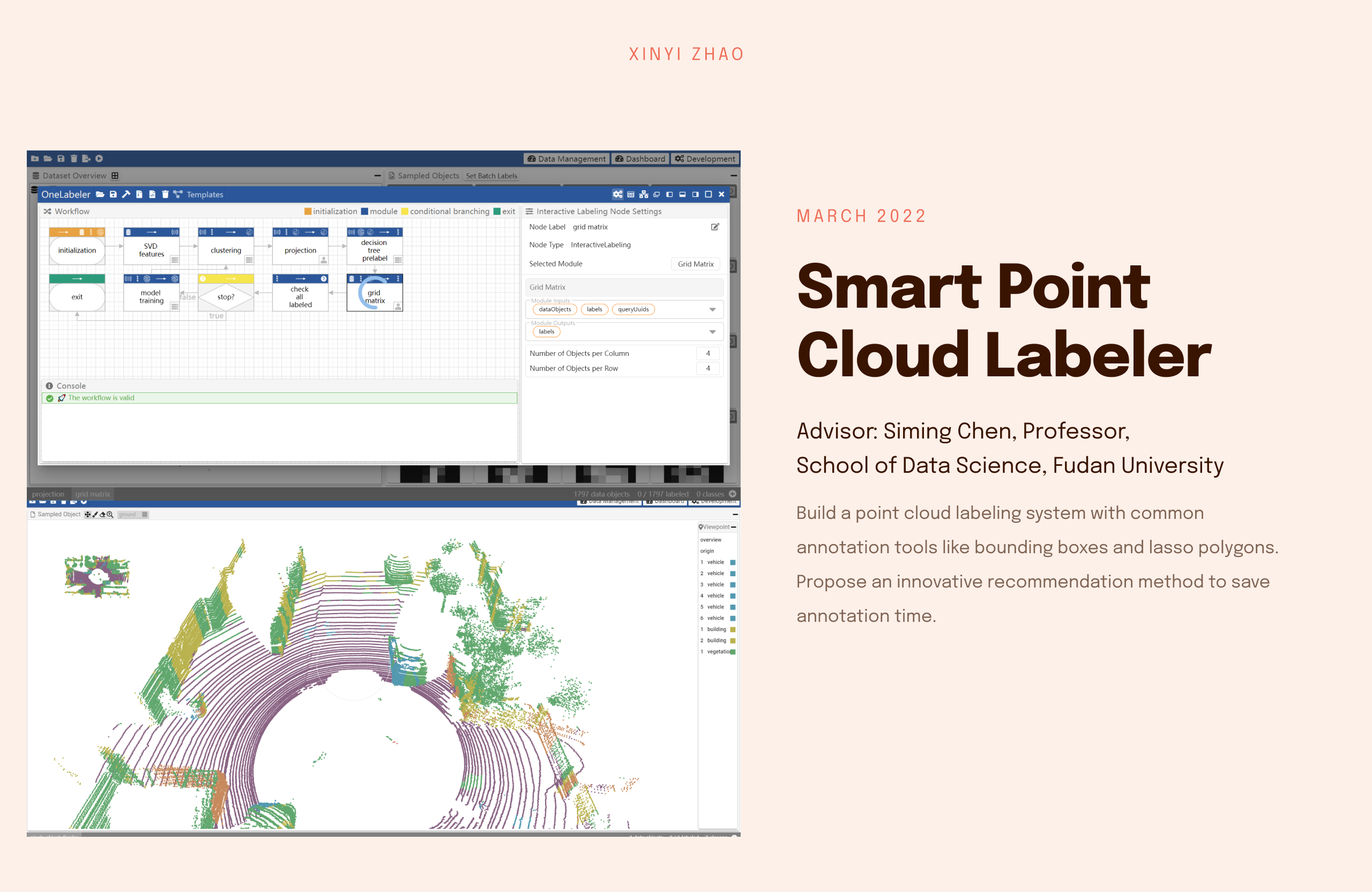
Intelligent Point Cloud Labeling with Viewpoint Recommendation
Jun 2021 - Nov 2022
Autonomous driving requires labeled 3D point cloud segmentation datasets to train models.
However, annotating point cloud segmentation is laborious.
The annotator has to label a large number of points, and frequently needs to adjust the viewpoint to navigate in the 3D space.

A 3D scene of KITTI point clouds, it's difficult to find a suitable view to observe.
Existing point cloud segmentation systems face the challenge of how to reduce annotators’ time cost of choosing a suitable viewpoint.
In this work, we defines that a good perspective is determined by the divisibility of the points under the modified perspective.
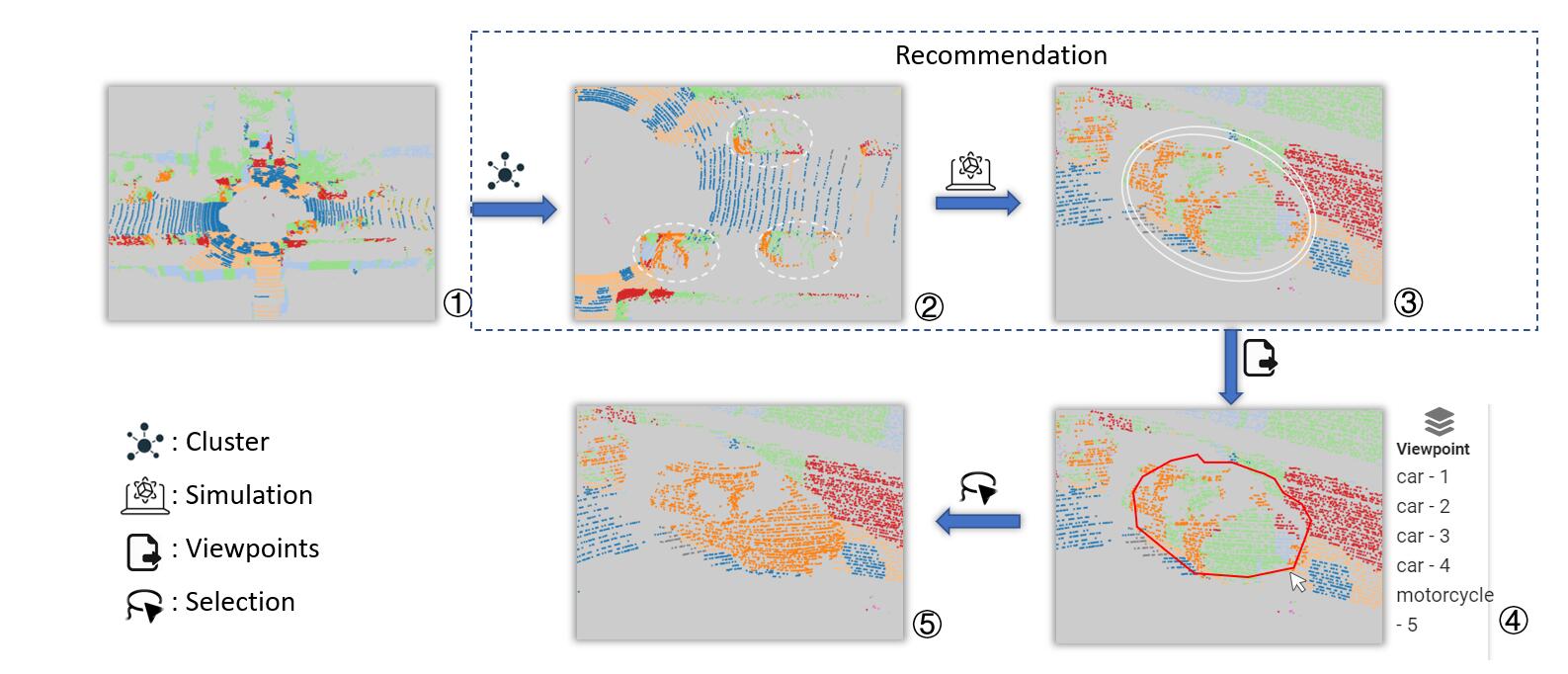
Our method enables effective navigation in autonomous driving point cloud data, based on the clustering center of data objects and simulation of human interaction to estimate annotation cost. (1): Point cloud interface. (2): Calculating center of each data objects for a particular category. (3): Simulating human interaction and estimating interaction cost. (4): Selecting a recommended view. (5): Annotation result under the recommended viewpoint.
The projection of 3D points should be explainable for annotators, while the points of different categories, at the same time, should be easy to separate.
We propose an intelligent viewpoint recommendation method. Our approach is based on the idea of finding minimum estimated human interaction cost under different camera angles.
We apply Fitts’ law to model the human interaction cost of lasso selection, and introduce a near-linear SVM classification to approximate the user selection range.
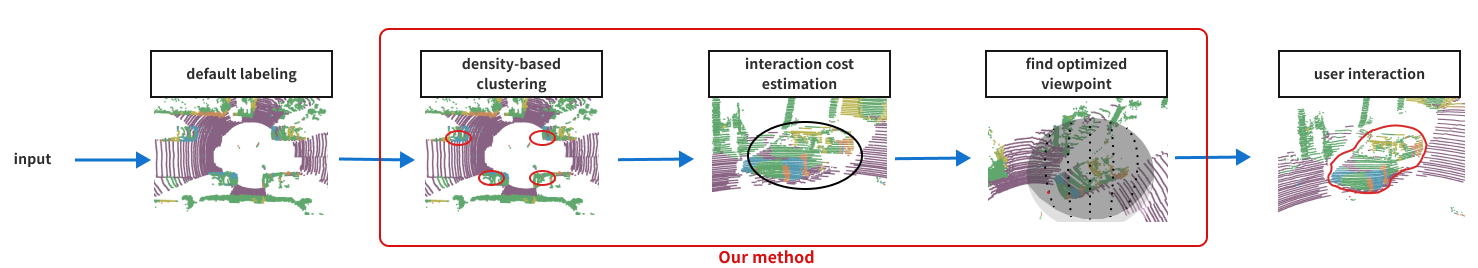
Workflow of our method. Based on the default labeling results to provide a feasible recommended viewpoint. The method will return the camera position and target to the front-head rendering system. (a) For each category, clustering the points based on scanning density. (b) Based on 2d projection using a near-linear SVM and get the tunnel’s perimeter and margin width. (c) Calculate interaction cost using Fitts’ law distance to solve the optimization problem. (d) Recommend viewpoint to the user, and user’s modification will be returned to the algorithm for update.
We built a point cloud annotation tool with a viewpoint recommend callback functions. We implemented models for default labeling and added some customization. We also made a recommendation list clicking to jump to recommended perspective with a bounding box highlighting the objects.
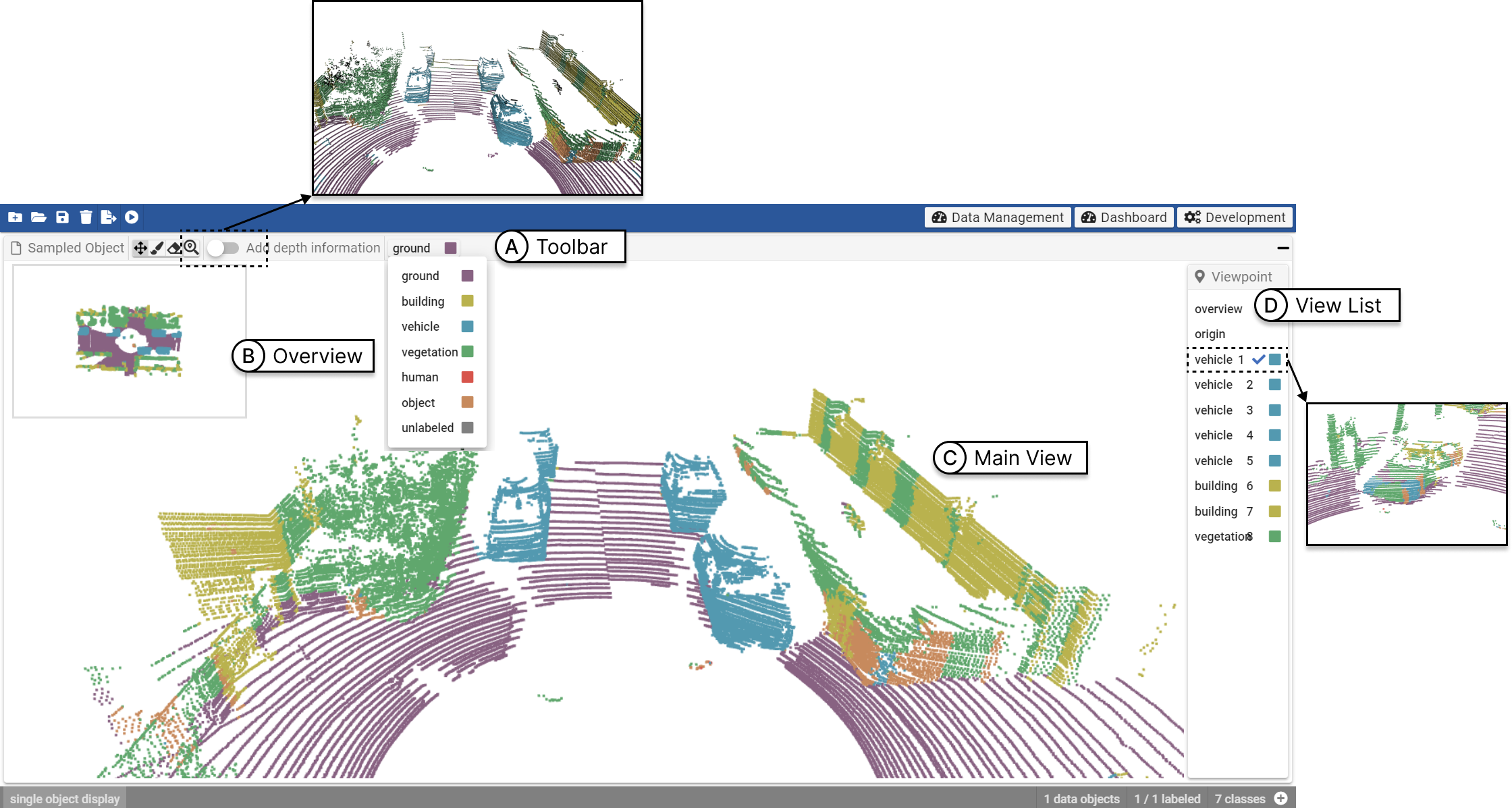
Interface of the point cloud labeling system. (A) Toolbar: a control toolbar where the user can switch between interaction modes (e.g., selection and zooming modes). (B) Scene overview: an overview of the point cloud data. (C) Point cloud annotation view: the workspace where the user annotates point cloud. (D) Viewpoint table view: a list showing recommended viewpoints.
We conduct a user study to compare our algorithm with other methods on different point cloud data.
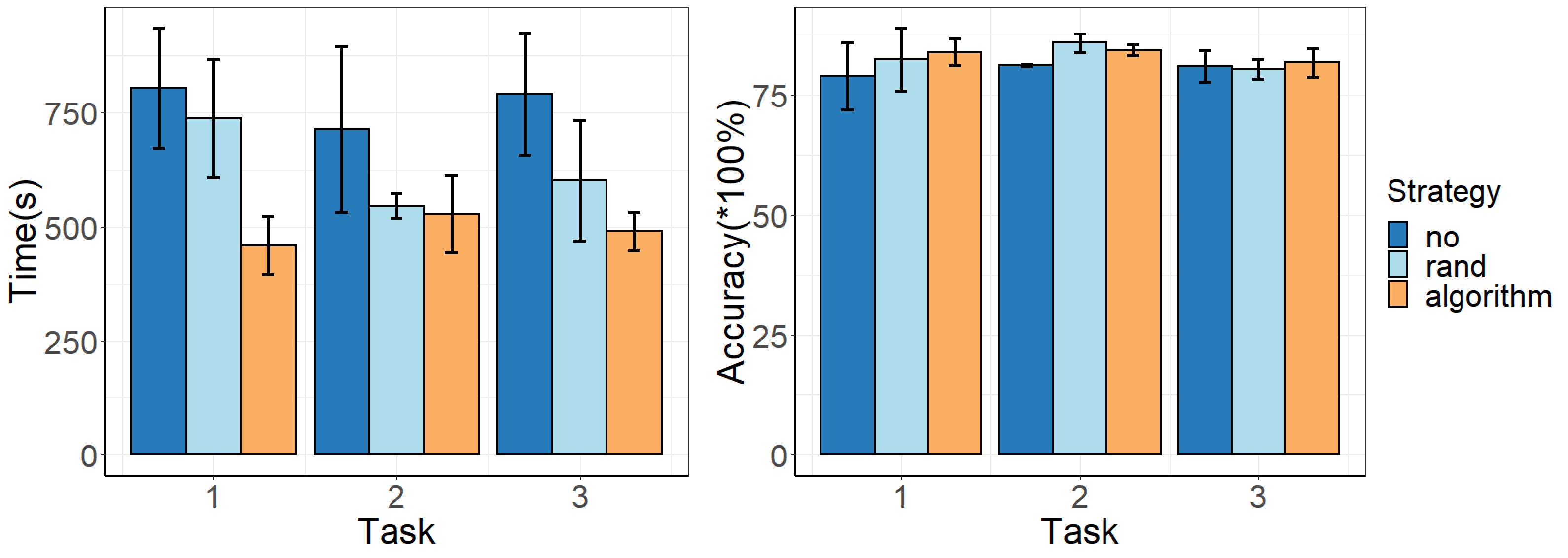
Comparison of completion time (left) and accuracy (right) on different strategies on three different point cloud.
The result confirms that our approach reduced the time cost to label point cloud segmentation.